
Race to 6G: Everything You Need to Know
Table of Contents
As we forge ahead in the world of wireless innovation, the emerging race to 6G marks a new chapter in our quest to expand communication frontiers. Join us as we unravel the complexities of 6G technology, shedding light on its pivotal features, international endeavors, and far-reaching applications. We also take a critical look at 6G’s lesser-known aspects, focusing on the concerns surrounding electromagnetic fields (EMF) and their implications for health and the environment. This exploration is not just about technological leaps; it’s a journey into the heart of our connected future and what conversations need to be had for a more sustainable telecommunications development.
Understanding 6G Technology
What is 6G?
Before we plunge into the race for 6G, it’s crucial to understand what 6G entails. Building on the foundation laid by 5G, 6G aims to revolutionize wireless communication, offering unprecedented speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive device connectivity. The evolution from 5G to 6G signifies a quantum leap in the capabilities of our interconnected world.
The Evolutionary Jump from 5G to 6G
As we transition to 6G, it’s essential to discern the key features that differentiate it from its predecessor. From amplified terahertz frequencies to breakthroughs in electromagnetic standards, the advancements in 6G promise a communication landscape characterized by unparalleled speed, efficiency, and reliability. 6G, the next evolution in wireless technology following 5G cellular networks, boasts the capability to harness higher frequencies, leading to significantly enhanced capacity and reduced latency compared to its predecessor.
6G’s Impact on Speed and Efficiency
A primary objective of 6G is to support ultra-fast, one-microsecond latency communications, a notable advancement that is 1,000 times quicker than the one-millisecond throughput achieved by 5G. Anticipated to revolutionize various domains, including imaging, presence technology, and location awareness, the 6G technology market holds the potential for substantial improvements. Through synergy with artificial intelligence (AI), the computational infrastructure of 6G is poised to discern optimal locations for computing activities, encompassing decisions related to data storage, processing, and sharing.
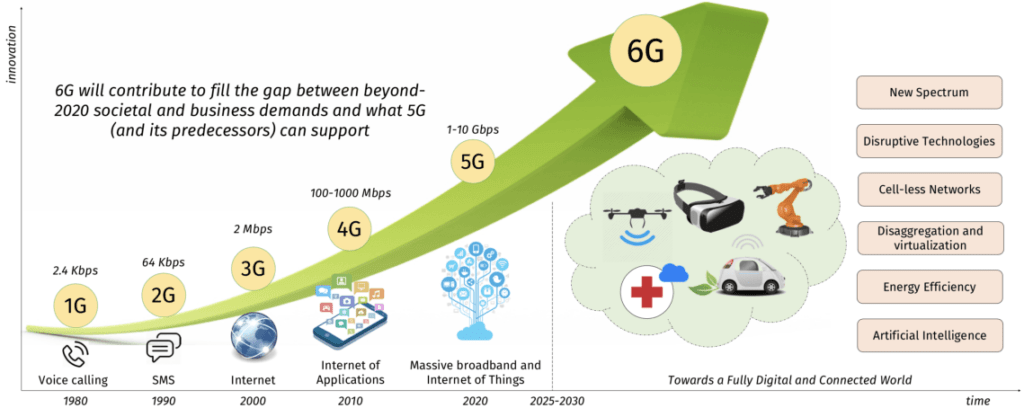
Image Source: Honor
Overview of Global Efforts in 6G Development
Potential Applications of 6G:
Examining the applications of 6G sheds light on its real-world impact. From empowering IoT ecosystems to revolutionizing healthcare and transportation, 6G’s potential applications underscore its significance in shaping the future. Within the domain of wireless communication, the emergence of 6G is anticipated to bring about groundbreaking advancements, ushering in innovative possibilities across diverse sectors:
- Immersive Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR): The seamless integration of 6G is poised to redefine AR/VR experiences. With improved data speeds and ultra-low latency, the technology is expected to enable immersive applications, ranging from virtual meetings to augmented reality gaming, ushering in a new era of interactive digital engagement.
- Precision Healthcare and Telemedicine: The combination of high-speed connectivity and low latency holds the promise of facilitating real-time remote surgeries, advanced telemedicine consultations, and the smooth transfer of substantial medical datasets.
- Autonomous Vehicles and Intelligent Transportation Systems: The automotive industry stands to benefit significantly from 6G advancements. There is also huge potential for 6G to propel autonomous vehicles and enhance intelligent transportation systems, ensuring safer and more efficient mobility solutions.
- Smart Cities and Infrastructure: The technology’s capacity to support a vast number of connected devices and facilitate swift data exchange can lead to enhanced urban planning, resource management, and overall efficiency in city infrastructure.
- Advanced Industrial Automation: The industrial landscape is poised for transformation with the integration of 6G. Enhanced connectivity and low latency are anticipated to power advanced automation processes, optimizing manufacturing, logistics, and supply chain operations.
- Immersive Entertainment and Gaming: The entertainment industry is set to undergo a paradigm shift with 6G. There is also potential for ultra-high-definition streaming, immersive gaming experiences, and innovative content delivery methods, redefining how audiences engage with entertainment.
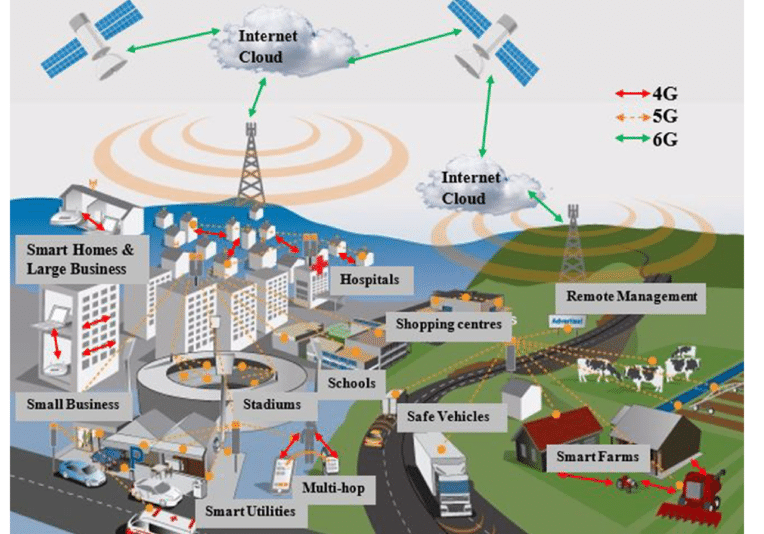
Image Source: ResearchGate
Challenges in 6G Development
While the prospects of 6G are promising, the journey is not without its challenges. This section delves into the technical hurdles, funding concerns, and regulatory issues that cast shadows on the path to 6G realization.
- Spectrum Scarcity: Limited spectrum in the terahertz bands requires advanced technologies like beamforming and massive MIMO to overcome issues like propagation loss.
- Energy Efficiency: The extensive data demands of 6G networks require sustainable solutions like energy harvesting and network slicing to ensure energy efficiency.
- Security and Privacy: Managing the vast amounts of data generated for ubiquitous connectivity requires robust mechanisms like encryption, blockchain, and federated learning to ensure security and privacy.
- Standardization and Regulation: Coordinating diverse stakeholders and complying with technical, legal, and ethical norms necessitates a clear and flexible framework for standardization and regulation.
- Social Acceptance and Impact: The introduction of novel communication forms raises ethical concerns. Engaging with the public and stakeholders is essential to align technology with human values and address questions of data ownership and fairness.
The Dark Side of 6G
While 5G mobile communication systems are currently being deployed, discussions on 6G technology have already commenced worldwide, accompanied by initial funding programs. Despite the historical trend of introducing new generations every decade, this analysis contends that introducing 6G labels at this juncture poses significant risks. Several reasons discourage early discussions on 6G:
- The absence of tangible technological advancements in a potential 6G system;
- The adaptability of the 5G communication system through softwarization concepts, allowing for regular updates; and
- Widespread 6G discourse could adversely affect the deployment and evolution of 5G, introducing entirely new business cases and customer ecosystems compared to its predecessors.
Looking ahead, as we don’t view 5G as the final milestone, we’ll offer insights into the future of mobile communication systems, detached from the current mainstream discourse. There are also cybersecurity threats & privacy concerns, emphasizing the need for robust security measures to safeguard individuals from potential risks.
Image Disclaimer: This AI-generated image is a creative exploration and does not represent actual expectations of 6G’s impact on society. It’s an artistic interpretation meant to provoke thought on technological advancement and its relationship with nature.
The Cautionary Tale of 6G: Lessons Unlearned
The world nears adopting 6G, urging reflection on overlooked lessons from 5G and 4G rollouts. These earlier technologies, despite their connectivity advancements, were deployed with little regard for environmental, ecological, and health impacts. There’s a growing apprehension that, like its predecessors, 6G is being ushered in with insufficient scrutiny towards its long-term consequences.
The deployment of 6G, much like 5G, involves the use of higher frequency bands. This escalation in frequency and the consequent electromagnetic radiation poses a significant risk, not just theoretically, but based on precedents set by earlier technologies. Studies have pointed out the potential health risks associated with prolonged exposure to EMFs, including issues like oxidative stress, increased risk of cancer, and fertility damage. Yet, the tech industry continues to accelerate its pace, prioritizing advancement over health.
Furthermore, the environmental and ecological impacts are alarming. 6G, like 5G, needs a dense transmitter network. This leads to higher energy use, posing challenges to global sustainability efforts. The potential harm to wildlife, particularly birds and insects sensitive to electromagnetic fields, is an issue that remains largely unaddressed. This technological leap forward is seemingly blind to the ecological footprints it leaves behind.
The rapid deployment of these technologies also raises questions about the ethical considerations in play. The digital divide, a glaring issue with 5G and 4G, is likely to be perpetuated with 6G. While some enjoy the benefits of cutting-edge technology, others are left in digital obscurity, widening social and economic disparities. The hasty rollout of these technologies often skips extensive public consultation. This leads to decisions without wide public awareness or agreement.
Regulating 6G: Policies and Governance
International Regulatory Landscape for 6G
Navigating the complex web of international regulations for 6G, this section provides insights into the regulatory landscape governing 6G development. The vision for a ubiquitous mobile network, providing connectivity everywhere, necessitates extensive wide area coverage. To achieve this, exploring higher spectrum ranges, especially terahertz bands, is deemed impractical for the next-generation mobile band. These bands suit the 6G vision, merging short-range radar with communication for an improved edge-to-user environment.
A supportive 6G spectrum mobile policy should prioritize the effective utilization of bands below 6GHz. This approach aims to catalyze:
- Research into advanced spectrum sharing in bands conducive to broad coverage, potentially down to the Internet Protocol (IP) level.
- Long-term replanning of the international spectrum allocations table, expanding adjacent mobile bands below 6GHz where feasible.
- Parallel spectrum refarming, seamlessly introduces new technologies while phasing out older ones in existing bands, rendering next-generation spectrum auctions obsolete.
- Preparing a sub-6GHz band for a unified network, merging satellite and terrestrial links to a consumer device.
- Readying a common terahertz (THz) band for converging sensing (radar) and very short-range communications.
- Development of a roadmap for transitioning to a 6G world with AI-driven spectrum sharing, possibly including regulation.
- Advancement of AI-powered ‘sleep mode’ to unprecedented levels, simultaneously enhancing spectrum sharing, supporting net-zero carbon objectives, and addressing exposure concerns.
Ethical Considerations in 6G Development and Deployment
Navigating 6G’s ethical landscape means addressing issues beyond just technical advancements. As the evolution towards 6G unfolds, it is crucial to incorporate ethical dimensions into the decision-making processes. The following aspects merit careful examination:
Privacy Concerns
Safeguarding user privacy is paramount. 6G’s vast connectivity and sensing yield large data volumes, raising concerns about potential misuse or unauthorized access to sensitive info. Implementing robust privacy mechanisms, including encryption and secure authentication, is imperative to uphold individuals’ privacy rights.
Data Ownership and Control
The proliferation of data in 6G networks raises questions about ownership and control. Establishing clear data ownership frameworks, ensuring user consent, and preventing control concentration are key for transparency and fairness.
Environmental Sustainability
The ethical implications of 6G extend to environmental sustainability. As technology advances, it is crucial to minimize the environmental impact, considering factors like energy consumption and electronic waste. Sustainable practices, such as energy-efficient network designs and responsible disposal of electronic components, should be prioritized.
Security and Resilience
Ethical considerations encompass ensuring the security and resilience of 6G networks. Robust cybersecurity and proactive steps are crucial to prevent harm and protect users.
The Race to 6G Continues
In pondering 6G’s future, we’re at a critical juncture, akin to 5G and 4G. Promising tech mustn’t neglect health and environmental concerns. Lessons from previous generations of wireless technology are not merely cautionary tales but essential guides for a more responsible approach.
In developing and deploying 6G, we must balance progress with ethical considerations, privacy safeguarding, and protection of all biological objects. Awareness of potential environmental impacts, security risks, and societal disparities is crucial. This urges aligning tech advancements with global well-being, ensuring 6G benefits society and protects our planet’s health.




